Bilateral agreements and strategic partnerships between BRICS countries
Due to the informal nature of BRICS, which is not institutionalized under international law, and the small number of legally binding treaties that the BRICS countries have concluded as a group, it is of particular interest how bilateral relations between the individual country pairs have developed since the first BRICS summit in 2009. Some country pairs within the BRICS group have significantly expanded their bilateral relations through legally binding agreements since the group's creation in 2009, while others have concluded few or no bilateral treaties. Some have formulated a strategic partnership action plan.
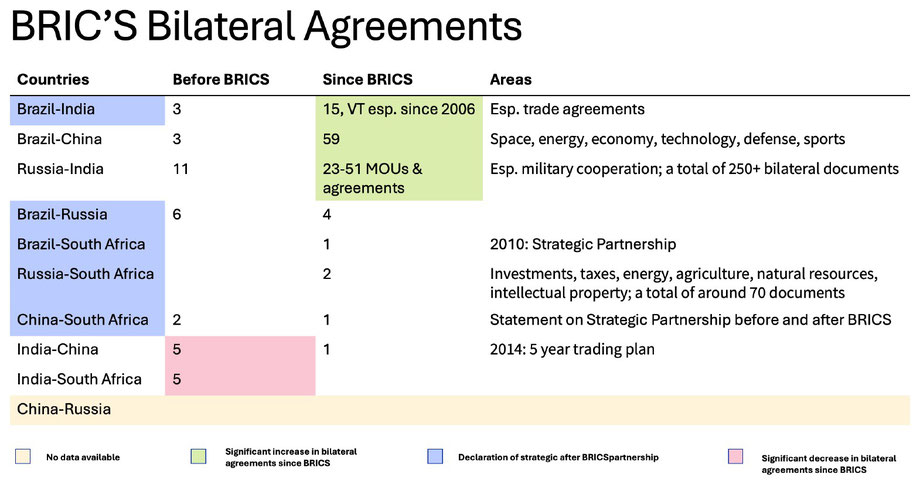
The following country pairs have concluded multiple bilateral agreements since 2009:
- Brazil and India concluded 15 bilateral agreements to strengthen their strategic partnership in 2020. The number of bilateral agreements between the countries has steadily increased after formulating a strategic partnership in 2006. The majority of these agreements are concerned with trade.
- Brazil and China concluded 13 cooperation agreements in 2009. In 2011, the countries concluded further 8 cooperation agreements and 13 economic agreements. Another 10 bilateral agreements followed in 2019, as well as 15 trade and partnership agreements in 2023. The two partners, therefore, have concluded 59 agreements since 2009, compared to only around 3 during the previous two decades. The agreements are related to space, energy, economics and finance, technology, defense, and sports.
- Russia and India had already concluded over 10 bilateral agreements before 2009. Since 2009, this number has more than doubled. In 2017, the countries concluded 21 bilateral agreements and another 28 Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs), and agreements followed in 2021. The known bilateral treaties between Russia and India mainly relate to military cooperation. However, after 1991, the treaty basis between the two states was updated and over 250 bilateral documents were signed, according to the governments.
The following countries have signed few or no bilateral agreements since 2009:
- Brazil and Russia: Overall, the number of bilateral contracts signed between Brazil and Russia did not increase significantly after the first BRICS summit in 2009.
- Brazil and South Africa solely signed a Strategic Partnership in 2010, when South Africa joined the BRIC group.
- India and China concluded most of their bilateral agreements before 2009, mainly in 2002. However, in 2014 they approved a Five-Year Development Program for Economic and Trade Cooperation.
- India and South Africa concluded most bilateral agreements before 2009.
- China and South Africa concluded most bilateral agreements before 2009.
The following countries have decided or confirmed their strategic partnership after 2009:
- Brazil and India
- Brazil and Russia
- Brazil and South Africa
- Russia and South Africa concluded two partnership agreements in 2013 and 2016. The bilateral relations between the two states are based on a solid legal platform of about 70 various documents and cover the spheres of investment protection, double taxation avoidance, energy, agriculture, exploration, mining and procession of natural resources, intellectual property etc.
- China and South Africa signed a declaration of strategic partnership in 2010, when South Africa joined the BRIC group. However, they had already signed a similar document in 2000.
Overall, researching bilateral agreements between the BRICS countries turned out to be quite difficult, as some of the data is not entirely publicly accessible and was not provided upon request. Therefore, the following is not an exhaustive list of the legally binding, bilateral agreements between the various BRICS countries. Therefore, not all contracts can be named in this document, but are mentioned only as contract packages, as more detailed information on these contracts is unfortunately not available. Data on bilateral agreements between Russia and China is missing. There is a large number of bilateral Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs), joint statements, and similar documents between the BRICS countries in which they express their common interest in advancing a particular issue. However, these documents are not legally binding. MOUs, joint statements, etc. have therefore not been included in this listing, but some of these expressions of interest have led to joint projects or working commissions and even bilateral contracts.
Literature
Embassy of India in Moscow (2024): Bilateral Relations. (https://indianembassy-moscow.gov.in/index.php [30.01.2024]).
Embassy of India, Brasilia, Brazil (2024): Bilateral Relations. (https://eoibrasilia.gov.in/index.php [30.01.2024]).
Embassy of the People's Republic of China in in the Republic of South Africa (2024): China-South Africa. (http://za.china-embassy.gov.cn/eng/ [30.01.2024]).
Embassy of the People's Republic of China in India (2024): China-India Relations. (http://in.china-embassy.gov.cn/eng/ [30.01.2024]).
Embassy of the Russian Federation in the Federal Republic of Brazil (2024): Russia - Brazil. (https://brazil.mid.ru/ru/ [30.01.2024]).
Government of India - Ministry of Commerce and Industry – Department of Commerce (2024): Trade Agreements. (https://commerce.gov.in/international-trade/trade-agreements/ [30.01.2024]).
High Commission of India, Pretoria, South Africa (2024): Bilateral Relations. (https://www.hcipretoria.gov.in [30.01.2024]).
Ministério das Relações Exteriores (2024): People’s Republic of China (https://www.gov.br/mre/en/subjects/bilateral-relations/all-countries/people-s-republic-of-china [30.01.2024]).
Ministério das Relações Exteriores (2024): Republic of South Africa. (https://www.gov.br/mre/en/subjects/bilateral-relations/all-countries/republic-of-south-africa [30.01.2024]).
Ministério das Relações Exteriores (2024): Republic of South India. (https://www.gov.br/mre/en/subjects/bilateral-relations/all-countries/republic-of-india [30.01.2024]).
Ministério das Relações Exteriores (2024): Russian Federation. (https://www.gov.br/mre/en/subjects/bilateral-relations/all-countries/russian-federation [30.01.2024]).
The Embassy of the Russian Federation in the Republic of India (2024): Russia and India. (https://india.mid.ru/en/ [30.01.2024]).